In stock
Muscle Relaxing Formula + CBD Oil 6%
Complete your selection
What is in Muscle Relaxing Formula + CBD Oil 6%
Any questions?
Our team of nutrition experts and scientists has the answers.
Following extraction, CBD is diluted in hemp seed oil.
Ordinarily, hemp seed oil contains very little CBD (0.0025%). CBD is mostly found in the flowers of Cannabis sativa and, to a lesser degree, the leaves, but not in the seeds. CBD Oil 10% therefore contains hemp seed oil to which CBD extracted from hemp flowers has been added.
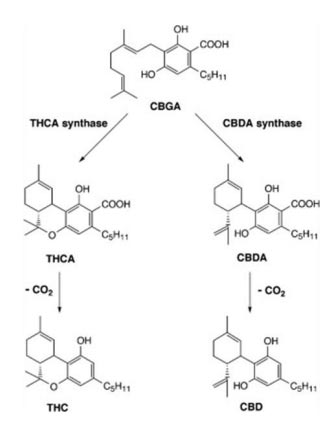
When cannabis grows, it produces THC-A and CBD-A, not THC or CBD. It is only when the two molecules are heated that they are decarboxylated into their active forms (27). The conversion of CBD-A into CBD can also be achieved more slowly by exposing the molecule to light, to heat (the temperature of gastric fluids is 37°C) or overtime (28). CBD Oil 10% contains CBD and not CBD-A, as well as small amounts of a number of other phytocannabinoids. There is currently no product on the market offering greater CBD oil benefits.
The hemp used in this product contains no THC. It therefore has no narcotic effect and has an excellent safety profile in humans.
Once ingested, CBD is quickly distributed around the body. Its lipophilic nature means it rapidly crosses the blood-brain barrier to reach tissues in the brain. It does not alter the heart rate and affects neither blood pressure nor body temperature. The half-life of CBD is 9 hours, after which it is eliminated vie urine in a metabolised form.
To date, there have been no public health problems reported with the use of a THC-free hemp oil standardised in CBD.
CBD Oil 10% can be combined with other supplements available to buy at Supersmart such as InflaRelief Formula, an enhanced formulation for relief of inflammation problems, with Natural Pain Relief, a natural, universal painkiller, and with Posinol 50 mg, an extract of Apocynum venetum which promotes mental relaxation.
This product’s capsules are composed of HPMC (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose), a plant substance derived from cellulose. HPMC is widely used for medicines and dietary supplements. It contains no animal ingredients, is recognised as safe by health authorities and is considered more sustainable than synthetic alternatives.
Muscle Relaxing Formula combines the four plant extracts most widely-studied in relation to muscle pain – and in their best form.
Lemon balm leaf.
Lemon balm is a medicinal herb traditionally used for over 2000 years to calm the nerves and ease pain. Recent clinical trials have confirmed the anxiolytic effects of lemon balm extract (1-3) as well as its ability to reduce sensitivity to pain via modulation of certain receptors in the central nervous system (4-6). Studies have demonstrated its analgesic properties (7-8) and associated decrease in sensitivity to external stimuli (nociception).
These properties are linked to the presence of terpenes in its essential oil as well as to its high content of phenolic compounds (rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid), citral, flavonoids (luteolin) and tannins (9).
Attention: many unscrupulous manufacturers replace the costly lemon balm extract with related species that smell strongly of lemon such as citronella or lemongrass.
The aerial parts of passionflower.
Passionflower contains several substances that act as pain-relievers: indole alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes and glucosides (10), although more than 294 volatile compounds have been identified.
The majority of pharmacological studies conducted on passionflower have demonstrated its effects on the central nervous system, particularly anxiolytic and sedative properties (11). Commission E (a European scientific advisory board) and ESCOP (the European Scientific Cooperative on Phytotherapy) also officially recognise the use of passionflower to reduce nervousness, and relieve muscle spasms and nerve pain.
The flowers of German camomile
Known for its relaxing properties, camomile has a number of anti-inflammatory and analgesic ingredients such as chamazulene, apigenin, flavonoids and alpha bisabolol. It has produced good results when administered to people suffering from various types of pain (12).
Attention: German camomile (Matricaria recutita), the flowers of which are the most beneficial parts, should not be confused with feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium), the leaves of which are used to reduce the intensity of headaches and migraines.
Valerian root.
Traditionally used by Native Americans for treating muscle injuries, valerian root is still in demand today. It contains more than 150 chemical compounds, including valerenic acid and valtrates which explain its effect on certain chemical messengers in the brain and its relaxing benefits (13).
The formulation also contains two micronutrients recognised for their physiological benefits for human health:
Vitamin E (natural form).
Well-known for its exceptional antioxidant benefits, vitamin E also has anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory properties
Attention: the most abundant form in the body is alpha-tocopherol. As the synthetic form of this molecule is much less well-absorbed, it’s important to choose supplements such as Muscle Relaxing Formula which contain the natural form (14).
Magnesium (in its most soluble and absorbable form).
Magnesium plays a role in nerve transmission and helps muscles relax after contracting. As well as this muscle-relaxant effect, it also participates in pain relief: by disrupting NMDA receptors, it impedes the entry of calcium ions into cells, producing an anti-nociceptive effect.
This effect is associated with decreased sensitivity to pain stimuli triggered by injuries or insult to tissues. Magnesium thus offers significant potential for reducing hypersensitivity to actual and phantom pain.(15-16).
Attention: The less absorbable a magnesium salt is, the less beneficial it will be for the body and the greater its laxative effect. It’s therefore essential to choose the best forms: magnesium citrate and magnesium chloride. It’s also important to control your magnesium intake from food if you are taking it in dietary supplement form.
To maximise this formulation’s efficacy, you can also follow these steps throughout the supplementation period:
- Make sure you stay well-hydrated by drinking at least two litres of water a day, a little at a time. Good hydration promotes healthy circulation in muscle fibres.
- Set aside time every day to relax (meditation, visualisation, listening to relaxing music, contemplation without stimuli, etc.) and ensure you get a good night’s sleep overwork and lack of sleep exacerbate pain.
- Avoid eating foods that promote systemic inflammation such as red meat, dairy products, cooked meats, processed foods and refined cereals.
- Prioritise anti-inflammatory foods, particularly those rich in omega-3 fatty acids (fats that are able to reduce pain) as well as fresh fruits and vegetables, all rich in antioxidants. You can combine Muscle Relaxing Formula with a daily dose of Super DHA, a natural formulation rich in omega-3 which provides a much higher intake than can be obtained from everyday diets.
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid molecule found in hemp (Cannabis sativa), just like the well-known psychotropic substance, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). However, unlike THC, CBD has no narcotic properties.
THC was the first psychoactive ingredient to be discovered in marijuana (1-3), but it was only in the 1990s that scientists identified the endogenous signalling system now known as the endocannabinoid system. This is a collection of endogenous messengers (endocannabinoids) and specific receptors located on external cell membranes (CB1 and CB2 receptors).
It works on a simple principle: when the body deems it necessary, endocannabinoid messengers are produced which bind to their corresponding receptors, triggering various cellular responses such as stimulation of appetite, limitation of synaptic transmission, anti-nociceptive effects (pain relief), hypothermia or reduction of spontaneous locomotion (4).
We know, for example, that endocannabinoids are effective at inhibiting the transmission of small-diameter nociceptive fibres (which are involved in the pain process) and at reducing the release of neurotransmitters such as substance P, which are responsible for the transmission of pain. What’s less straightforward is how this system influences several complex mechanisms such as neuroplasticity, apoptosis, neuroinflammation and traumatic memory.
It so happens that plants produce molecules that have a strong resemblance to endocannabinoids, so much so that they are able to bind to the same receptors (with varying degrees of affinity). Some of them, including THC, produce cellular responses which are very similar to – or even greater than - those triggered by endocannabinoids.
Cannabis contains more than 200 types of molecule that mimic endocannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD) which may account for up to 40% of the plant’s dry extract.
Need help?
You may also like















