Complete your selection
The anti-stress supplement Peptidyss® is a fish protein hydrolysate obtained from deep ocean fish using a cutting-edge enzymatic process.
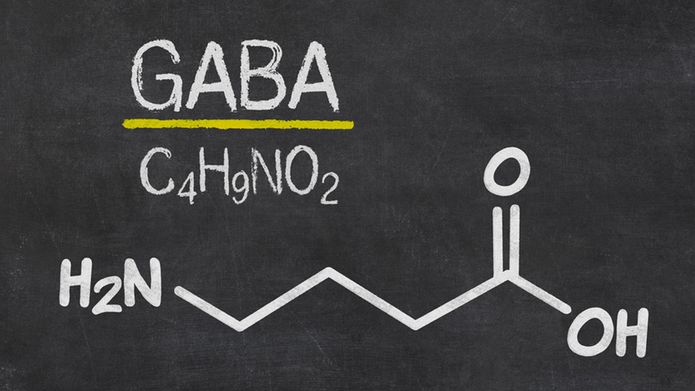
Made up of 18 amino acids with a molecular weight of less than 1,000 daltons, its peptides act as precursors to regulatory neuropeptides and neurotransmitters of the nervous system, including endorphins, serotonin and melatonin. These play a major role in mood and stress management. Its compounds have also been shown to modulate the concentration of GABA, a neurotransmitter that inhibits excitatory nerve signals emitted, in particular, in situations of anxiety or strong emotion.
How does Peptidyss® fish protein hydrolysate work in the body?
With its innovative formulation, Peptidyss® acts at various levels of the nervous system.
First of all, it influences levels of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Discovered by Eugene Roberts and Sam Frankel in the 1950s, this inhibitory neurotransmitter acts to slow down nerve cell activity by binding to specific receptors (called GABAA and GABAB). Highly-abundant in cerebral cortex neurons, it governs behaviour and emotional stability, which appears tested in the event of anger, irritability or aggression (1). It thus counterbalances the excitatory potential of glutamate – from which it is nonetheless made (2).
At the same time, the peptides in Peptidyss® act as a precursor to several chemical mediators intrinsically linked to well-being:
- endorphins: The best-known of these, beta-endorphin, alters perception of pain and stress (3-4) ;
- serotonin: known as the ‘happy hormone ’, this important neuromediator governs self-control and inhibition (5) ;
- melatonin: synchronised with the day-night cycle, this neurohormone regulates the body’s internal clock. Released by the pineal gland at particular times, its production increases at bedtime, peaking during the night (6).
It’s worth mentioning that, unlike certain allopathic tranquillisers, fish protein hydrolysates do not cause drowsiness or a lack of alertness.
A fish peptide supplement with proven efficacy
The supplement Peptidyss® has been the subject of various scientific publications to support its mode of action:
- adaptability to stress. In a study on rats, the effects of a standard anxiolytic were compared with those of hydrolysed fish proteins, both at rest and in a situation of acute stress. Levels of adrenaline, noradrenaline, ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) and GABA in the hypothalamus and hippocampus were all measured (7);
- cognitive abilities. Other studies have also looked at the impact of fish protein hydrolysates on cognitive function (learning, memorisation, concentration (8).
What is in Peptidyss®
Any questions?
Our team of nutrition experts and scientists has the answers.
There are various natural measures that can help you manage day-to-day stress better:
- take time to relax. Deep breathing exercises (such as cardiac coherence) or mindfulness meditation increase GABA production and help you feel more at ease (9) ;
- take regular exercise. When sufficiently long and intense, physical activity has been shown to increase circulating levels of beta-endorphin (10) ;
- adopt an anti-stress diet. Certain foods promote the release of endorphins, dopamine and/or serotonin in the brain and thus produce a feeling of pleasure. These include chocolate with a high cocoa content (80% minimum), bananas, brown rice, eggs, pulses or nuts (11-12). Note that GABA is naturally present in chestnuts, potatoes and certain types of tea;
- laugh (or smile). In a similar way to exercise, the jolts produced by a good laugh trigger the release of endorphins (13). If you are very tense, the simple act of smiling, even if forced, may be enough to generate positive emotions and reduce anxiety;
- open up to someone. If you are plagued by anxiety or chronic stress, articulating your suffering can help put you on a path to inner peace. Speak to a trusted family member, friend or health professional;
- establish a bedtime routine. If you suffer from stress-related sleep disorders, initiate a calming routine before bed. In the evening, turn off any screens to avoid blue light exposure and instead engage in peaceful activities (such as reading). Before you go to sleep, try writing down any worrying thoughts – it will help stop you ruminating and make it easier to fall asleep;
- get enough sleep. It’s essential to give yourself sufficient sleep time (7-8 hours a night) in order to recover physically and mentally, and thus be able to cope better with stressful situations ( (14).
This product’s capsules are made of pullulan, a natural polysaccharide obtained by fermenting tapioca or corn. Pullulan contains no animal ingredients and provides an excellent barrier to oxygen, helping to preserve the integrity of the capsule’s ingredients. It is also an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic materials.
- Suntheanine®, an L-Theanine supplement extracted from green tea, is based on the thousand-year-old Zen tradition of the Japanese (15) ;
- Adrenal Support, a complex of adaptogen and medicinal plants, contains amongst others, tulsi which helps maintain resistance to stress (16) ;
- during periods of intense stress, consider supplementing with magnesium, a mineral that plays a role in normal psychological function. The synergistic supplement Optimag contains 8 forms of magnesium chosen for their optimal bioavailability (17).
Need help?
You may also like
of experience
your money back
##montant## purchase